Wire rope is a type of cable made up of several strands of wire tightly wound together around a larger core. Often, you will hear the words “wire” and “rope” used to refer to “wire rope.” However, they are not technically the same. Instead, only cables that are at minimum 9.52 mm thick qualify as wire rope. Read More…
As leading innovative wire rope manufacturers, Bergen Cable Technology has been providing engineering assistance for well over half a century, helping customers develop cost effective, durable solutions.

Lexco is an ISO:9001 manufacturer of wire rope, cable, and bungee cord assemblies; and push-pull controls. Our in-house capabilities range from swaging and extrusions to die-casting, proof-loading, and CNC machining. Lexco Cable is proud to serve a diverse set of markets including military, aerospace, OEM, MRO, marine, architectural, and more. Contact us today.
At Kennedy Wire Rope & Sling Company, we take pride in being a trusted source for high-performance wire ropes that keep industries moving safely and efficiently. We engineer and supply wire rope solutions that meet the rigorous demands of lifting, rigging, and load-handling applications across construction, marine, energy, and industrial markets.

Aero Assemblies, Incorporated strives to make every effort, as dedicated wire rope manufacturers, to maximize product value throughout the manufacturing process.

At Zauderer Associates, Inc., we specialize in providing high-quality wire rope solutions designed for durability, safety, and reliability across diverse industries. With extensive experience and technical expertise, we offer a comprehensive range of wire ropes tailored to meet rigorous performance requirements.

More Wire Rope Companies
Applications
Wire rope manufacturers engineer their products to deliver exceptional load-bearing capacity, making wire rope a superior and versatile alternative to traditional materials such as manila or hemp rope. High-strength wire rope is utilized extensively in industries where safety, reliability, and durability are crucial. Applications for industrial wire rope include lifting, baling, tie-down, hoisting, hauling, towing, mooring, anchoring, rigging, cargo control, guidance systems, and counterbalancing. Wire rope assemblies are also vital for railings, fencing, guardrails, and fall protection systems.
Curious about what specific applications wire rope is best suited for? Wire rope is indispensable for a wide range of heavy-duty industrial applications. In construction, it is used for cranes, elevators, and hoisting structural elements. In mining and forestry, wire rope facilitates the movement of heavy loads and equipment in challenging environments. The marine industry relies on stainless steel wire rope and galvanized cable for mooring, ship rigging, and offshore oil and gas drilling platforms, where corrosion resistance is paramount. Industrial manufacturing uses wire rope for overhead cranes, conveyor systems, and automated machinery.
Other significant industries taking advantage of wire rope technology include agriculture (for fencing and baling), fitness and sports equipment (such as plastic-coated cables for gym machines or playgrounds), electronics (for tensioning and support), theater and entertainment (for rigging stage equipment with black powder-coated cables), transportation (including cable cars and bridges), security (lock cables and barriers), healthcare (for patient lifts), and consumer goods (pet leashes, clotheslines, and DIY uses).
Read all about Wire Ropes on “Cable 101”
The History of Wire Rope
Wire rope, as we recognize it today, boasts a rich history spanning nearly two centuries. The innovation dates back to between 1831 and 1834, when German mining engineer Wilhelm Albert sought to enhance safety and efficiency in the Harz Mountains’ mining operations. Albert’s original design featured four three-stranded wires, which provided unprecedented strength compared to the previously used natural fiber ropes and metal chains.
The history of modern wire rope further evolved when L.D.B. Gordon, inspired by Albert’s invention, encouraged Robert Stirling Newall in Dundee, Scotland, to invent a wire rope manufacturing machine. Newall’s machine successfully produced four-strand wire ropes, each strand containing four wires, enabling large-scale production and innovation. Gordon, Newall, and Charles Liddell established R.S. Newall and Company, and in 1840, Newall secured a patent for “certain improvements in wire rope and the machinery for making such rope.”
American innovation followed closely. In 1841, John A. Roebling began producing wire rope for suspension bridges, enhancing the safety and feasibility of long-span structures. Around the same time, Josiah White and Erskine Hazard of the Lehigh Coal & Navigation Company (LC&N Co.) introduced wire rope to coal mining and railroad transportation projects. The use of wire rope in the Ashley Planes Project in Pennsylvania in 1848 dramatically reduced return times for coal cars, increasing both efficiency and capacity.
Wire rope’s impact was felt globally, particularly in 1874 when Adolf Bleichert & Co. pioneered bi-cable aerial tramways for mining in Germany’s Ruhr Valley. These technological advancements later found applications in military transportation for the German Imperial Army and the Wehrmacht, eventually spreading across Europe and the United States.
Since the 1800s, wire rope technology has continually advanced. Modern improvements include the use of high-tensile steel, advanced coatings for corrosion resistance (like galvanization), and specialized wire rope constructions for enhanced flexibility and strength. Today, wire rope remains an essential component in infrastructure, transportation, energy, and industrial processes worldwide, forming the backbone of our modern built environment.
Design
Production Process
Wire rope is manufactured by tightly twisting or braiding individual metal wires into strands, which are then helically wrapped around a central core. The number of wire filaments in each strand can range from two to dozens, depending on the application’s requirements for tensile strength, flexibility, and load-bearing capacity.
A key aspect of wire rope construction is the core. The core can be a fiber rope, a wire strand core (WSC), or an independent wire rope core (IWRC). For applications demanding maximum strength and fatigue resistance—such as crane cables, elevator cables, or heavy-lift slings—the IWRC is often preferred. An IWRC typically increases a wire rope’s overall strength by at least 7.5%, enhances flexibility, and helps prevent crushing or distortion under load.
Materials
Wire ropes can be engineered from a variety of metals to match their intended use. While specialty ropes may incorporate aluminum, nickel, copper, titanium, or bronze, the most common material by far is steel—valued for its exceptional strength, ductility, and fatigue resistance. Steel wire rope types include galvanized wire rope, bright (ungalvanized) wire rope, stainless steel wire rope, and cold-drawn carbon steel wire rope.
Galvanized steel wire rope is favored for outdoor, marine, and corrosive environments, as the zinc coating provides long-lasting protection against rust and abrasion. Stainless steel wire rope is chosen for applications where superior corrosion resistance is required, such as in food processing, chemical plants, and marine rigging. Bright wire rope, which is ungalvanized, is used in non-corrosive indoor settings, while cold-drawn carbon steel wire rope offers high tensile strength for demanding lifting and pulling tasks.
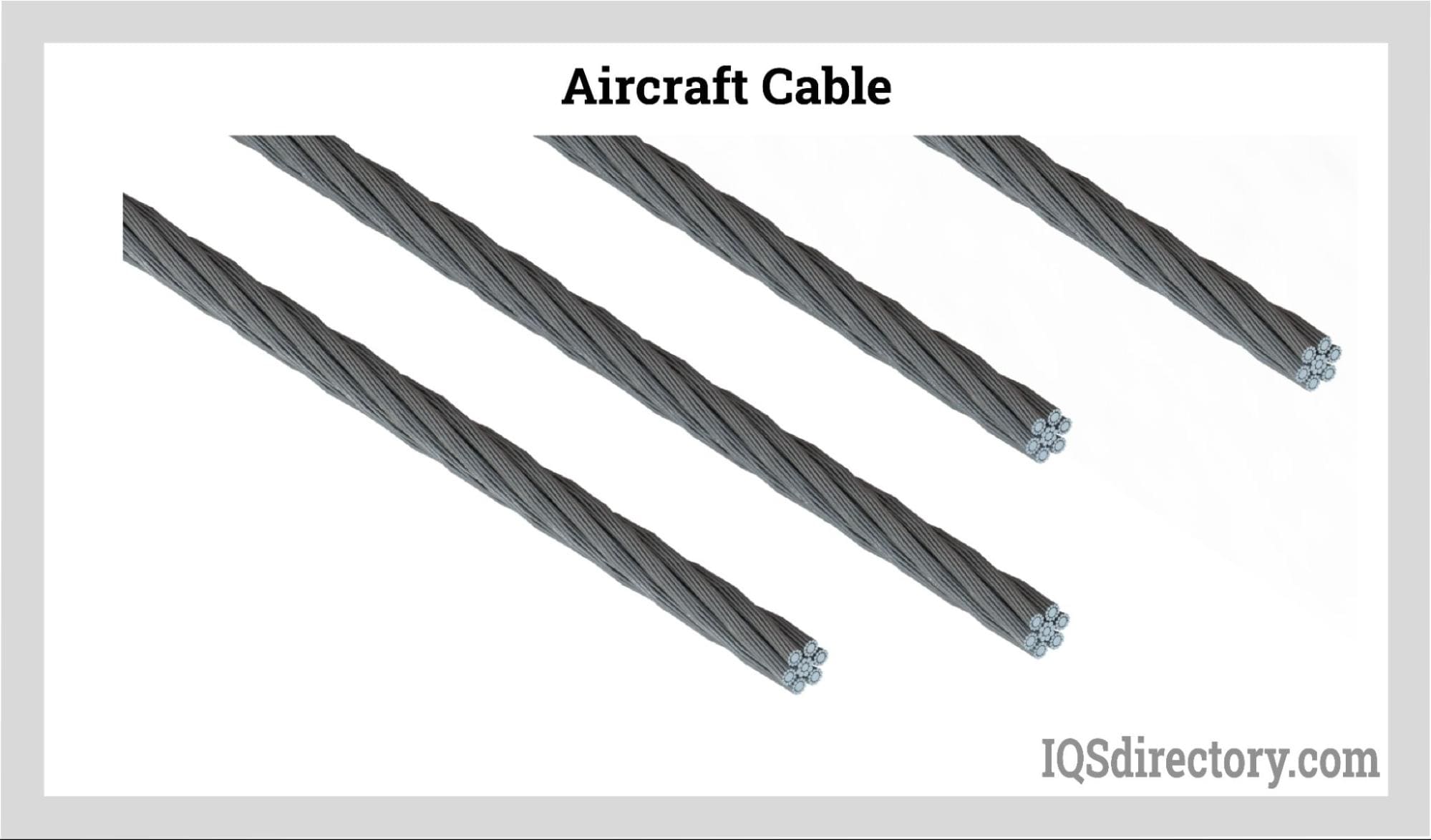
In aerospace and aviation industries, galvanized aircraft cable is used for control cables, safety cables, and emergency systems due to its optimal balance of strength, flexibility, and corrosion resistance.
Design Considerations and Customization
When selecting or specifying a custom wire rope, it’s essential to consider a range of design factors:
- Operating Environment: Will the wire rope be exposed to moisture, saltwater, chemicals, or extreme temperatures?
- Corrosion and Rust Resistance: Is a galvanized or stainless steel finish necessary?
- Flexibility vs. Strength: Does the application require extra pliability for pulleys or maximum tensile strength for lifting?
- Diameter and Breaking Strength: What are the minimum strength requirements, and what is the intended safety factor?
- Rotation-Resistance: Is the cable required to resist spinning or twisting under load?
- End Fittings and Terminations: Are there specific hardware or attachment requirements?
Manufacturers can further customize wire rope by color-coding for easy identification, adding corrosion-resistant coatings, or incorporating plastic sheathing to prevent fraying and wear when cables are routed over pulleys or exposed to repeated abrasion.
Are you trying to determine which wire rope design is best for your application? Consult with a wire rope supplier or manufacturer to discuss your specific needs, load requirements, and safety standards.
Types
Wire rope is classified according to the number of strands and number of wires per strand—a system that allows end-users to quickly gauge the cable’s strength, flexibility, and suitability for different tasks. Wire rope distributors and suppliers also provide technical specifications regarding core type, construction, length, weight limit, and accessory compatibility.
Here are the most common wire rope configurations:
- 6 x 19, 6 x 25, 6 x 26, 6 x 36: These constructions feature six strands, each with 19, 25, 26, or 36 wires, respectively. The 6 x 19 is popular for its balance of flexibility and abrasion resistance, making it ideal for winches, cranes, and general-purpose lifting.
- 7 x 7, 7 x 19, 19 x 7: These cables are often used in aircraft, control cables, and marine applications. 7 x 19 construction, in particular, is known for its flexibility and is frequently used for garage doors, sailboat rigging, and exercise equipment.
Looking for a specific wire rope type? Browse our directory of wire rope manufacturers or read more below for details on specialized cable options.
Wire rope can also be identified by more detailed codes indicating core type (e.g., IWRC, WSC), lay direction (right hand, left hand), and weight limit. Many wire rope suppliers also offer a comprehensive range of wire rope hardware—including connectors, fasteners, pulleys, turnbuckles, and fittings—to suit a variety of installation and safety requirements.
Other notable wire rope types include:
- Cable Wire Rope: Heavy-duty, multi-filament steel cable, commonly used in construction, industrial lifting, and rigging. Steel cable is essential for load-bearing applications where both strength and minimal stretch are required.
- Spiral Wire Rope: Constructed with strands twisted in the opposite direction of the inner core, spiral wire rope excels at blocking moisture and contaminants, making it suitable for harsh or outdoor environments.
- Stranded Rope: Made of spirally wound strands with crisscrossing layers for enhanced strength. Core options include wire rope, wire strand, or fiber, each offering different benefits in terms of flexibility and load capacity.
- Wire Rope Chain: Composed of linked segments for flexibility, but may be less robust than continuous strand wire rope for certain mechanical applications.
- Wire Rope Sling: Manufactured from improved plow steel wire for lifting slings, bridle slings, and endless slings. These slings feature enhanced durability and safety, with options for various terminations such as thimbles, chokers, and hooks.
Need help choosing the right wire rope type for your project? Contact a supplier or manufacturer to discuss your load and application requirements, and to compare cost, performance, and longevity across different cable constructions.
Advantages of Wire Rope
Wire rope offers a multitude of benefits for both industrial and commercial users. Its inherently robust design ensures even weight distribution across all strands, making it ideally suited for lifting and hoisting extremely heavy loads. Unlike synthetic ropes, wire rope is highly resistant to abrasion, crushing, and impact, resulting in a significantly longer service life under demanding conditions.
Among the key advantages of using wire rope:
- Exceptional Durability: When properly matched to the application and maintained, wire rope can withstand harsh environments, including exposure to chemicals, saltwater, and extreme temperatures.
- High Tensile Strength: Able to support substantial weights, making it the go-to choice for cranes, elevators, and hoisting equipment.
- Flexibility and Versatility: Wire rope is available in a range of diameters, constructions, and core types, allowing for customization to fit virtually any use case.
- Safety: Modern wire rope is engineered to minimize the risk of sudden failure, with built-in safety factors and compliance with strict industry standards.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Although the upfront cost may exceed that of synthetic ropes, the extended service life and lower maintenance requirements make wire rope a cost-effective choice over time.
- Corrosion Resistance: Galvanized and stainless steel wire ropes are specifically designed to resist rust and deterioration, ensuring reliable performance even in marine or outdoor environments.
Still have questions about the benefits of wire rope vs. synthetic alternatives? Learn more or contact a manufacturer for expert guidance tailored to your industry.
Accessories
Wire rope systems often rely on a comprehensive selection of accessories and hardware to ensure performance, safety, and ease of installation. Common wire rope accessories include:
- Clips (Wire Rope Clamps or Cable Clamps): Used for creating eye terminations or securing the loose end of a rope, vital for rigging and load-securing.
- Carabiners: Metal connectors with secure gate mechanisms, enabling rapid and safe attachment of wire rope to other structures or anchor points.
- Fittings (Turnbuckles, Swage Fittings): Turnbuckles provide tension adjustment, while swage fittings allow for permanent, high-strength terminations using mechanical or hydraulic pressing.
- Fasteners (Bolts, Nuts): Essential for attaching wire rope assemblies to machinery, buildings, or other equipment.
- Shackles and Hooks: Facilitate safe connections between wire rope and lifting devices, cranes, or anchoring systems.
- Thimbles: Protect the eye of a wire rope from wear and deformation, especially at high-stress connection points.
- Chokers: Used in lifting and rigging to create adjustable loops or slings.
Choosing the right accessory is critical for maximizing system reliability and safety. Are you unsure which fittings or hardware best suit your application? Review product specifications or consult with a wire rope distributor for recommendations tailored to your needs.
Proper Care for Wire Rope
Maintaining the quality and safety of your wire rope requires regular inspection, cleaning, and proper storage. Here are best practices for wire rope care:
- Inspect Regularly: Look for signs of wear such as fraying, kinks, broken wires, rust, or corrosion. Pay close attention to high-stress areas, bends, and terminations.
- Lubricate as Needed: Use appropriate lubricants to reduce internal friction and protect against moisture. Proper lubrication extends service life and maintains flexibility.
- Match Rope to Task: Always use the correct wire rope type and diameter for the intended application. Avoid overloading by respecting rated load and breaking strength specifications.
- Store Properly: Keep wire rope in a dry, clean environment away from corrosive agents, chemicals, and direct sunlight. Coil wire rope neatly to prevent kinks or crushing.
- Handle with Care: Use proper tools and techniques for installation and removal. Avoid dragging wire rope over abrasive surfaces or sharp edges.
Following these steps will significantly increase the longevity and reliability of your wire rope assemblies. For more information, explore our wire rope care guide or contact a service specialist.
Standards
Industry standards for wire rope and wire rope assemblies play a vital role in ensuring safety, consistency, and performance across diverse applications. Notable organizations such as the Wire Rope Technical Board (WRTB), ASTM International, ISO, and the American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME) provide comprehensive wire rope specifications and guidelines.
Key aspects governed by these standards include:
- Minimum Breaking Strength: Ensures ropes meet or exceed required load capacities for safety-critical tasks.
- Fatigue Resistance: Tests for durability under repeated bending and stress cycles.
- Corrosion Protection: Specifies coatings and treatments to extend lifespan in harsh environments.
- Construction Requirements: Defines acceptable rope constructions, diameters, tolerances, and core types for compatibility and interchangeability.
- Quality Control and Traceability: Mandates inspection, testing, and certification for consistent performance and accountability.
- Installation and Use: Outlines best practices for safe handling, installation, and maintenance to prevent accidents and failures.
Compliance with recognized standards not only safeguards users and operators but also simplifies the selection, replacement, and maintenance of wire rope assemblies. Regular audits, third-party inspections, and certifications help verify adherence to industry guidelines, instilling confidence in the quality and reliability of wire rope products.
Are you concerned about industry standards or certification requirements for your wire rope application? Engage with a manufacturer that adheres to leading standards and can provide documentation for your project.
How to Find the Right Manufacturer
Choosing the right wire rope manufacturer or supplier is crucial to ensure you receive a product that meets rigorous safety, quality, and performance requirements. Here’s a step-by-step guide to help you make an informed decision:
- Research and Shortlist: Begin by browsing our comprehensive directory of wire rope manufacturers. Review company profiles, product offerings, and industry expertise.
- Evaluate Capabilities: Look for manufacturers with experience in your specific industry or application (e.g., crane cables, marine rigging, mining, or aerospace). Consider their ability to provide custom solutions and meet specialized standards.
- Contact Multiple Suppliers: Select three or four companies to discuss your requirements. Share details on load capacity, environment, certifications, and any customizations needed.
- Inquire About Lead Times and Delivery: Ask about production timelines, inventory availability, and shipping options to ensure prompt fulfillment of your order.
- Compare Responses: Assess how each manufacturer addresses your needs in terms of technical support, compliance, pricing, and customer service. Look for companies that offer added value, such as recommendations for accessories, maintenance, or installation support.
- Request Documentation: Obtain product datasheets, certifications, and references to verify quality and compliance with industry standards.
Ultimately, the best manufacturer will be one that not only meets your technical requirements and budget but also demonstrates a commitment to safety, customer satisfaction, and ongoing support.
Ready to request a quote or start your project? Contact a wire rope manufacturer today and experience the benefits of working with a trusted industry leader.
What are the primary applications of wire rope?
Wire rope is used in a wide range of heavy-duty industrial applications including lifting, hoisting, towing, mooring, anchoring, rigging, cargo control, baling, tie-down, counterbalancing, and guidance systems. Other uses include railings, fencing, guardrails, and fall protection systems across industries such as construction, mining, marine, manufacturing, agriculture, transportation, and more.
How has wire rope technology evolved over time?
Wire rope technology dates back to the early 19th century, originating with Wilhelm Albert in Germany. Innovations such as wire rope manufacturing machines, the use of high-tensile steel, and advanced coatings for corrosion resistance have significantly improved strength, flexibility, and durability. Today, wire rope is an integral part of many modern industries worldwide.
What materials are used in wire rope construction?
While wire ropes can include metals like aluminum, nickel, copper, titanium, and bronze, most are made from steel. Steel wire ropes can be galvanized, bright (ungalvanized), stainless steel, or cold-drawn carbon steel, each chosen for its particular strength, flexibility, and corrosion resistance properties.
How do I choose the right wire rope for my application?
Selecting the right wire rope involves considering factors such as operating environment, corrosion resistance, flexibility, diameter, breaking strength, rotation resistance, and required end fittings. Consulting with a wire rope supplier or manufacturer can help ensure the appropriate design and specifications for your intended use and safety standards.
What are the common types and constructions of wire rope?
Wire rope is typically classified by strands and wires per strand, such as 6 x 19, 6 x 25, 7 x 19, or 19 x 7. Other types include cable wire rope, spiral wire rope, stranded rope, wire rope chain, and wire rope slings. Construction type, core material, and lay direction also affect performance and suitability for different tasks.
What are the main advantages of using wire rope?
Wire rope offers exceptional durability, high tensile strength, flexibility, safety, cost-effectiveness, and corrosion resistance. Its design provides even weight distribution, making it ideal for lifting heavy loads and withstanding abrasion, crushing, and impact in demanding industrial conditions.
How should wire rope be maintained for safety and longevity?
Wire rope maintenance includes regular inspection for wear and damage, lubrication to reduce friction and protect against moisture, proper selection for the task, correct storage away from corrosive elements, and careful handling during installation and use. Following these practices helps ensure long service life and reliable performance.
What accessories and hardware are commonly used with wire rope?
Wire rope systems often include accessories such as clips (clamps), carabiners, turnbuckles, swage fittings, fasteners (bolts and nuts), shackles, hooks, thimbles, and chokers. These components are critical for secure installation, system reliability, and safe operation in rigging and lifting applications.







 Cranes
Cranes Electric Hoists
Electric Hoists Forklifts
Forklifts Hydraulic Lifts
Hydraulic Lifts Rope
Rope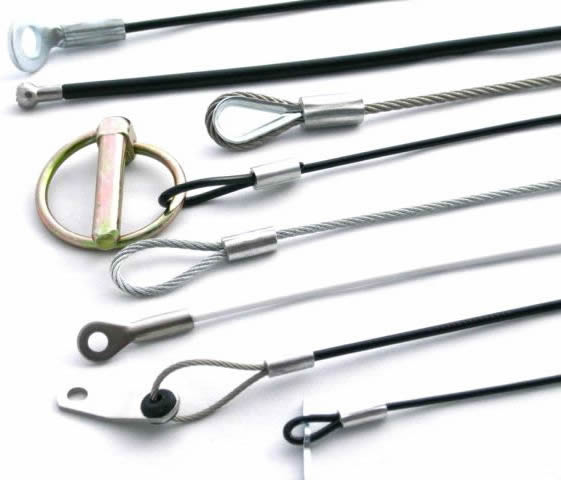 Wire Rope
Wire Rope Castings & Forgings
Castings & Forgings Bulk Material Handling
Bulk Material Handling Electrical & Electronic Components
Electrical & Electronic Components Flow Instrumentation
Flow Instrumentation Hardware
Hardware Material Handling Equipment
Material Handling Equipment Metal Cutting Services
Metal Cutting Services Metal Forming Services
Metal Forming Services Metal Suppliers
Metal Suppliers Motion Control Products
Motion Control Products Plant & Facility Equipment
Plant & Facility Equipment Plant & Facility Supplies
Plant & Facility Supplies Plastic Molding Processes
Plastic Molding Processes Pumps & Valves
Pumps & Valves Recycling Equipment
Recycling Equipment Rubber Products & Services
Rubber Products & Services